nifi-kafka-druid-earthquake-data
|
This demo only runs in the |
This demo will
-
Install the required Stackable operators.
-
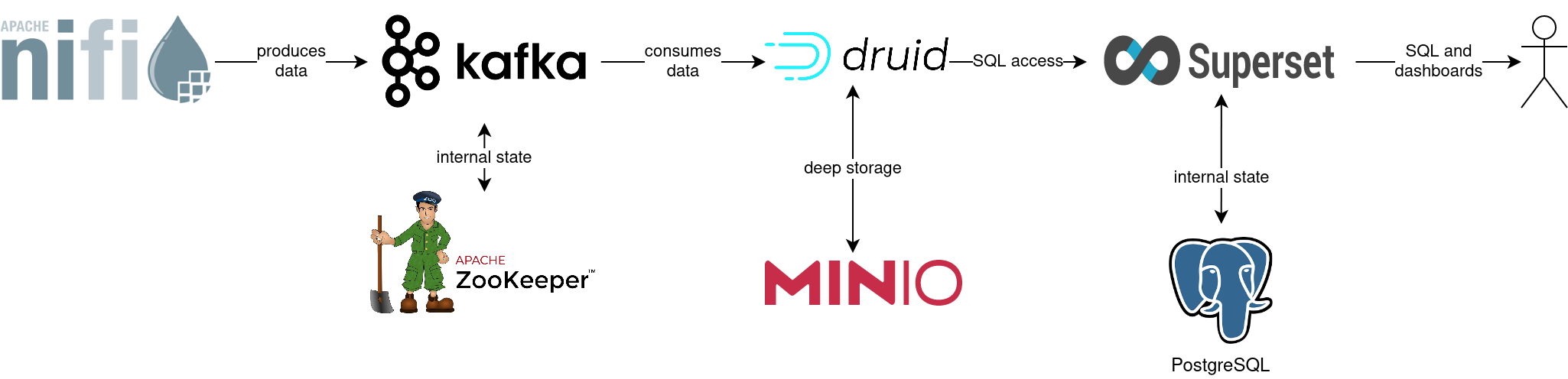
Spin up the following data products:
-
Superset: A modern data exploration and visualization platform. This demo utilizes Superset to retrieve data from Druid via SQL queries and build dashboards on top of that data
-
Kafka: A distributed event streaming platform for high-performance data pipelines, streaming analytics and data integration. This demo uses it as an event streaming platform to stream the data in near real-time.
-
NiFi: An easy-to-use, robust system to process and distribute data. This demo uses it to fetch earthquake data from the internet and ingest it into Kafka.
-
Druid: A real-time database to power modern analytics applications. This demo uses it to ingest the near real-time data from Kafka, store it and enable access to the data via SQL.
-
MinIO: A S3 compatible object store. This demo uses it as persistent storage for Druid to store all the data.
-
-
Continuously emit approximately 10,000 records/s of earthquake data into Kafka.
-
Start a Druid ingestion job that ingests the data into the Druid instance.
-
Create Superset dashboards for visualization of the data.
The whole data pipeline will have a very low latency, from putting a record into Kafka to showing up in the dashboard charts. You can see the deployed products and their relationship in the following diagram:
System Requirements
To run this demo, your system needs at least:
-
9 cpu units (core/hyperthread)
-
28GiB memory
-
75GiB disk storage
Listing Deployed Stacklets
To list the installed Stackable services run the following command:
$ stackablectl stacklets list
┌───────────┬─────────────┬───────────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Product ┆ Name ┆ Namespace ┆ Endpoints │
╞═══════════╪═════════════╪═══════════╪════════════════════════════════════════════════╡
│ druid ┆ druid ┆ default ┆ broker-metrics 172.18.0.2:32002 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ broker-https https://172.18.0.2:32304 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ coordinator-metrics 172.18.0.2:32058 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ coordinator-https https://172.18.0.2:32545 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ historical-metrics 172.18.0.2:30277 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ historical-https https://172.18.0.2:30903 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ middlemanager-metrics 172.18.0.2:32459 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ middlemanager-https https://172.18.0.2:31967 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ router-metrics 172.18.0.2:31720 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ router-https https://172.18.0.2:32656 │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ kafka ┆ kafka ┆ default ┆ metrics 172.18.0.2:31501 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ kafka-tls 172.18.0.2:31237 │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ nifi ┆ nifi ┆ default ┆ https https://172.18.0.2:31214 │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ superset ┆ superset ┆ default ┆ external-superset http://172.18.0.2:30677 │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ zookeeper ┆ zookeeper ┆ default ┆ zk 172.18.0.2:32682 │
├╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┼╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌╌┤
│ minio ┆ minio-druid ┆ default ┆ http http://172.18.0.2:31516 │
│ ┆ ┆ ┆ console-http http://172.18.0.2:30835 │
└───────────┴─────────────┴───────────┴────────────────────────────────────────────────┘|
When a product instance has not finished starting yet, the service will have no endpoint. Depending on your internet connectivity, creating all the product instances might take considerable time. A warning might be shown if the product is not ready yet. |
Inspecting Data in Kafka
Kafka is an event streaming platform to stream the data in near real-time. All the messages put in and read from Kafka are structured in dedicated queues called topics. The test data will be put into a topic called earthquakes. The records are produced (put in) by the test data generator and consumed (read) by Druid afterwards in the same order they were created.
As Kafka has no web interface, you must use a Kafka client like hhttps://github.com/edenhill/kcat[kafkacat]. Kafka uses mutual TLS, so clients
wanting to connect to Kafka must present a valid TLS certificate. The easiest way to obtain this is to shell into the
kafka-broker-default-0 Pod, as we will do in the following section for demonstration purposes. For a production setup,
you should spin up a dedicated Pod provisioned with a certificate acting as a Kafka client instead of shell-ing into the
Kafka Pod.
Listing Available Topics
You can execute a command on the Kafka broker to list the available topics as follows:
kubectl exec -it kafka-broker-default-0 -c kafka -- /bin/bash -c "/stackable/kcat -b localhost:9093 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.key.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.key -X ssl.certificate.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.crt -X ssl.ca.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/ca.crt -L"
Metadata for all topics (from broker -1: ssl://localhost:9093/bootstrap):
1 brokers:
broker 1001 at 172.18.0.2:32175 (controller)
1 topics:
topic "earthquakes" with 8 partitions:
partition 0, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 1, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 2, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 3, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 4, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 5, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 6, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001
partition 7, leader 1001, replicas: 1001, isrs: 1001You can see that Kafka consists of one broker, and the topic earthquakes with eight partitions has been created. To
see some records sent to Kafka, run the following command. You can change the number of records to print via the -c
parameter.
kubectl exec -it kafka-broker-default-0 -c kafka -- /bin/bash -c "/stackable/kcat -b localhost:9093 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.key.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.key -X ssl.certificate.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.crt -X ssl.ca.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/ca.crt -C -t earthquakes -c 1"
{
"time": "1950-01-09T13:29:32.340Z",
"latitude": 35.033,
"longitude": -116.8816667,
"depth": 6,
"mag": 2.42,
"magType": "ml",
"nst": 5,
"gap": 238,
"dmin": 0.848,
"rms": 0.48,
"net": "ci",
"id": "ci3361965",
"updated": "2016-01-28T18:07:12.280Z",
"place": "20km NE of Barstow, CA",
"type": "earthquake",
"horizontalError": 3.29,
"depthError": 31.61,
"magError": 0.181,
"magNst": 6,
"status": "reviewed",
"locationSource": "ci",
"magSource": "ci"
}If you are interested in how many records have been produced to the Kafka topic so far, use the following command. It
will print the last record produced to the topic partition, formatted with the pattern specified in the -f parameter.
The given pattern will print some metadata of the record.
$ kubectl exec -it kafka-broker-default-0 -c kafka -- /bin/bash -c "/stackable/kcat -b localhost:9093 -X security.protocol=SSL -X ssl.key.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.key -X ssl.certificate.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/tls.crt -X ssl.ca.location=/stackable/tls_server_mount/ca.crt -C -t earthquakes -o -8 -c 8 -f 'Topic %t / Partition %p / Offset: %o / Timestamp: %T\n'"
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385011 / Timestamp: 1680607795568
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385012 / Timestamp: 1680607795568
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385013 / Timestamp: 1680607795570
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385014 / Timestamp: 1680607795570
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385015 / Timestamp: 1680607795571
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385016 / Timestamp: 1680607795571
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385017 / Timestamp: 1680607795571
Topic earthquakes / Partition 0 / Offset: 385018 / Timestamp: 1680607795571If you calculate 385,011 records * 8 partitions, you end up with ~ 3,080,088 records. The output also shows that the
last measurement record was produced at the timestamp 1680607795568, which translates to Di 4. Apr 13:29:55 CEST 2023
(using the command date -d @1680607795).
NiFi
NiFi is used to fetch earthquake data from the internet and ingest it into Kafka. This demo includes a workflow ("process group") that downloads a large CSV file, converts it to individual JSON records and produces the records into Kafka.
Viewing testdata-generation Job
You can have a look at the ingestion job running in NiFi by opening the endpoint https from your
stackablectl stacklets list command output. In this case, it is https://172.18.0.3:32558. Open it with your favourite
browser. Suppose you get a warning regarding the self-signed certificate generated by the
Secret Operator (e.g. Warning: Potential Security Risk Ahead). In that case, you must
tell your browser to trust the website and continue.
Log in with the username admin and password adminadmin.
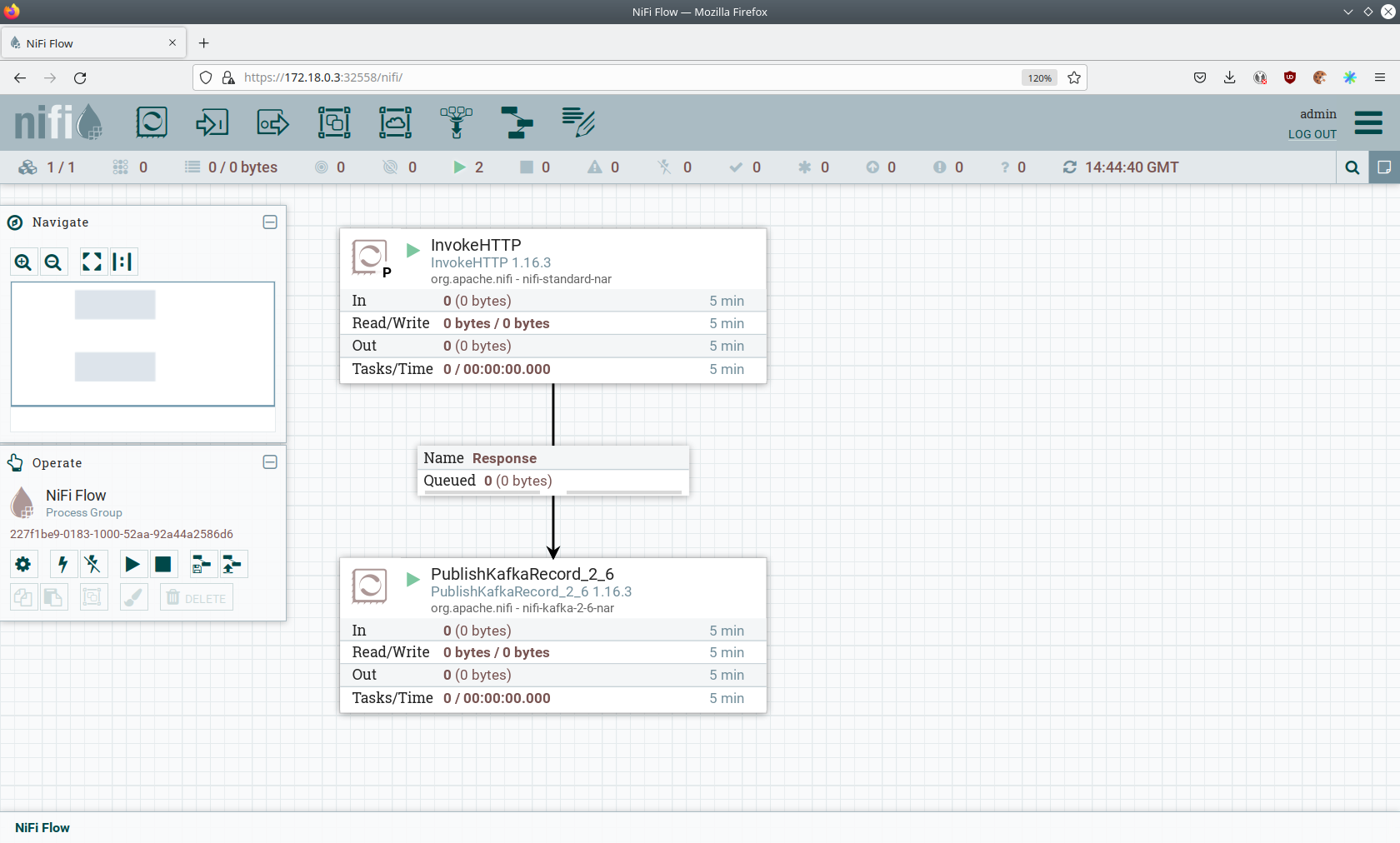
You can see the started ProcessGroup consisting of two processors. The first one - InvokeHTTP, fetches the CSV file
from the Internet and puts it into the queue of the next processor. The second processor - PublishKafkaRecord_2_6,
parses the CSV file, converts it to JSON records and writes them out into Kafka.
Double-click on the InvokeHTTP processor to show the processor details.
Head over to the Tab PROPERTIES.
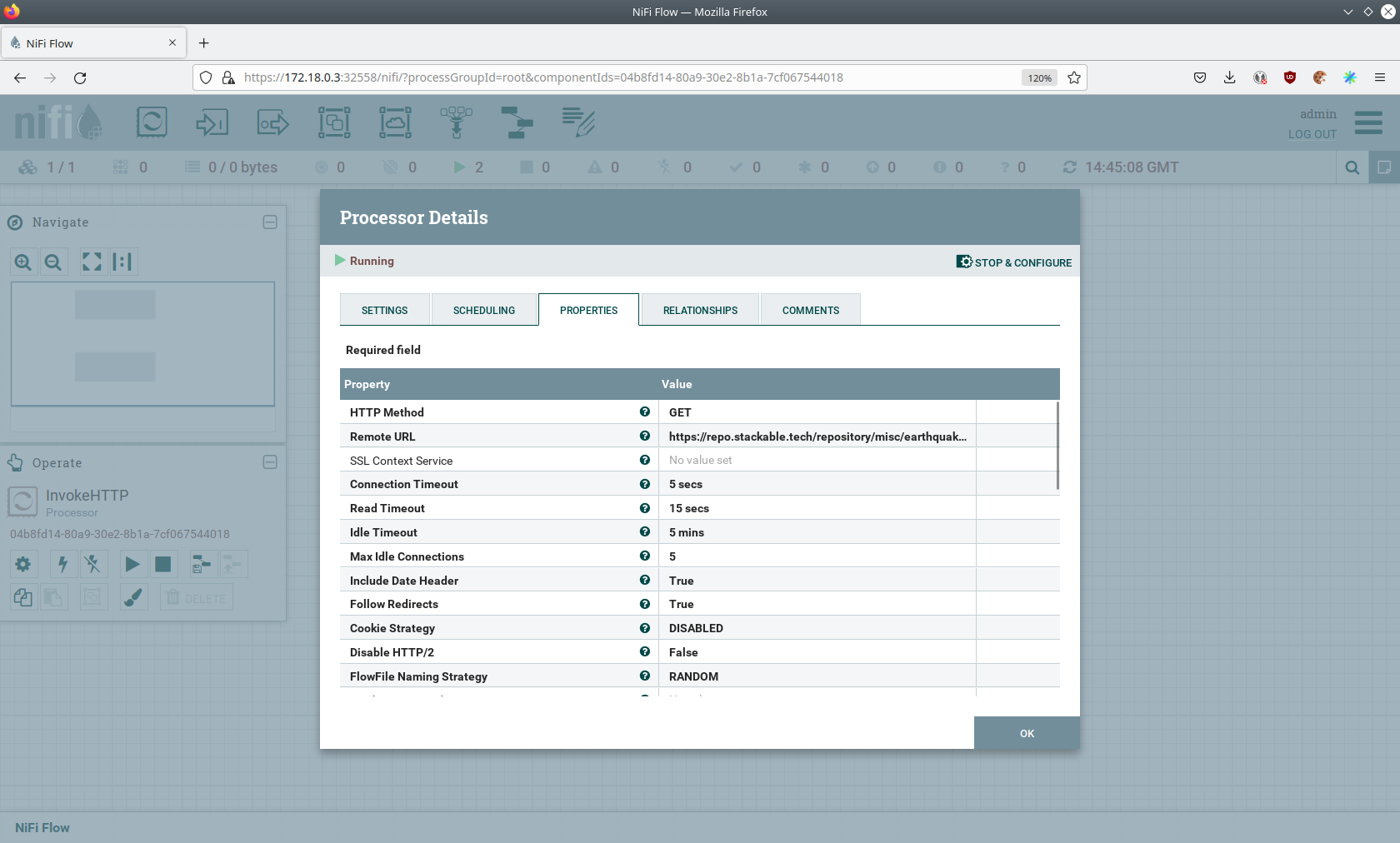
Here, you can see the setting Remote URl, which specifies the download URL from where the CSV file is retrieved. Close
the processor details popup by clicking OK. Afterwards, double-click on the processor PublishKafkaRecord_2_6.
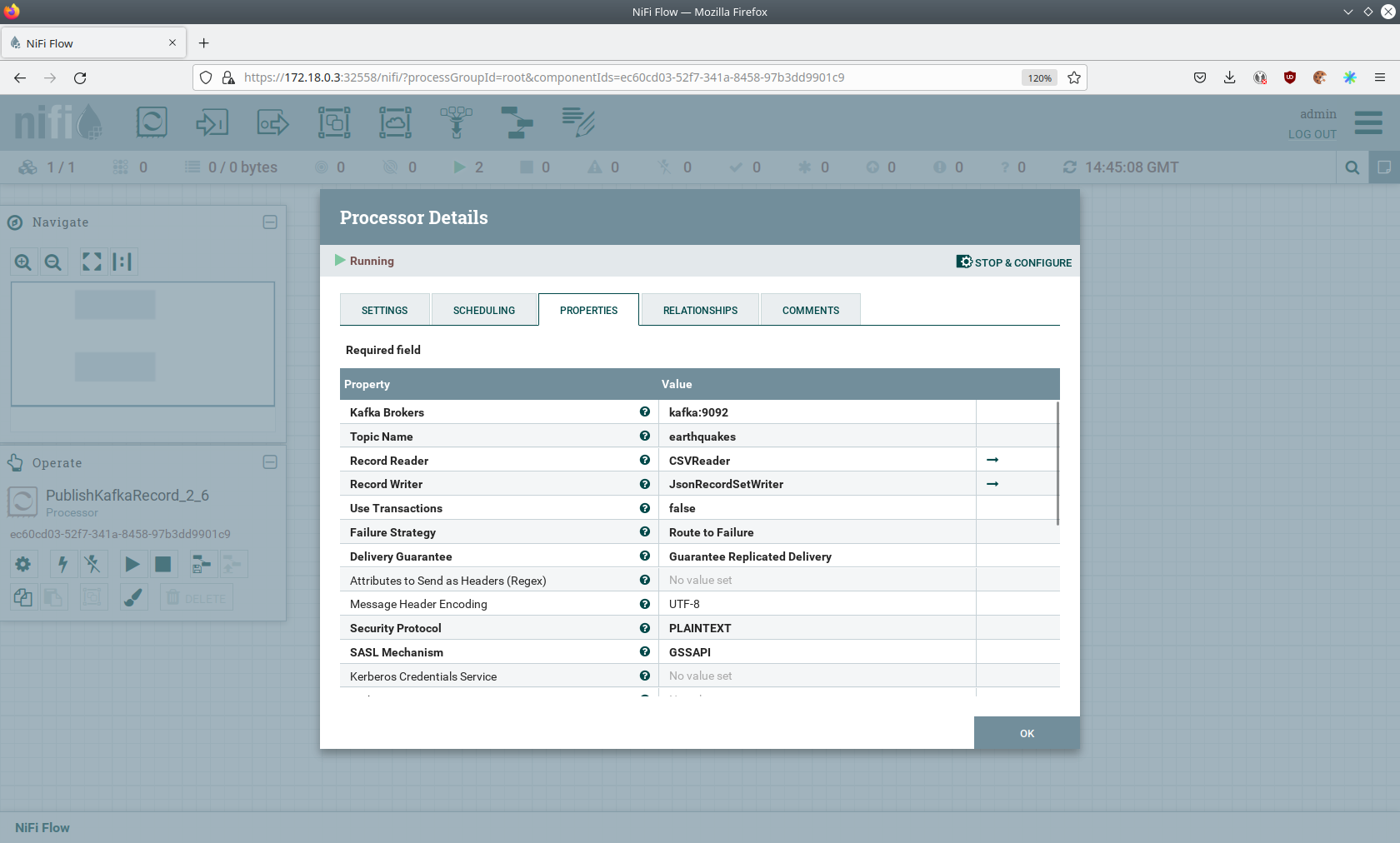
The Kafka connection details within this processor - like broker addresses and topic names - are specified. It uses the
CSVReader to parse the downloaded CSV and the JsonRecordSetWriter to split it into individual JSON records before
writing it out.
Druid
Druid is used to ingest the near real-time data from Kafka, store it and enable SQL access. The demo has started an ingestion job reading earthquake records from the Kafka topic earthquakes and saving them into Druid’s deep storage. The Druid deep storage is based on the S3 store provided by MinIO.
Viewing Ingestion Job
You can have a look at the ingestion job running in Druid by opening the endpoint router-http from your
stackablectl stacklets list command output (http://172.18.0.4:30109 in this case).
By clicking on Ingestion at the top, you can see the running ingestion jobs.
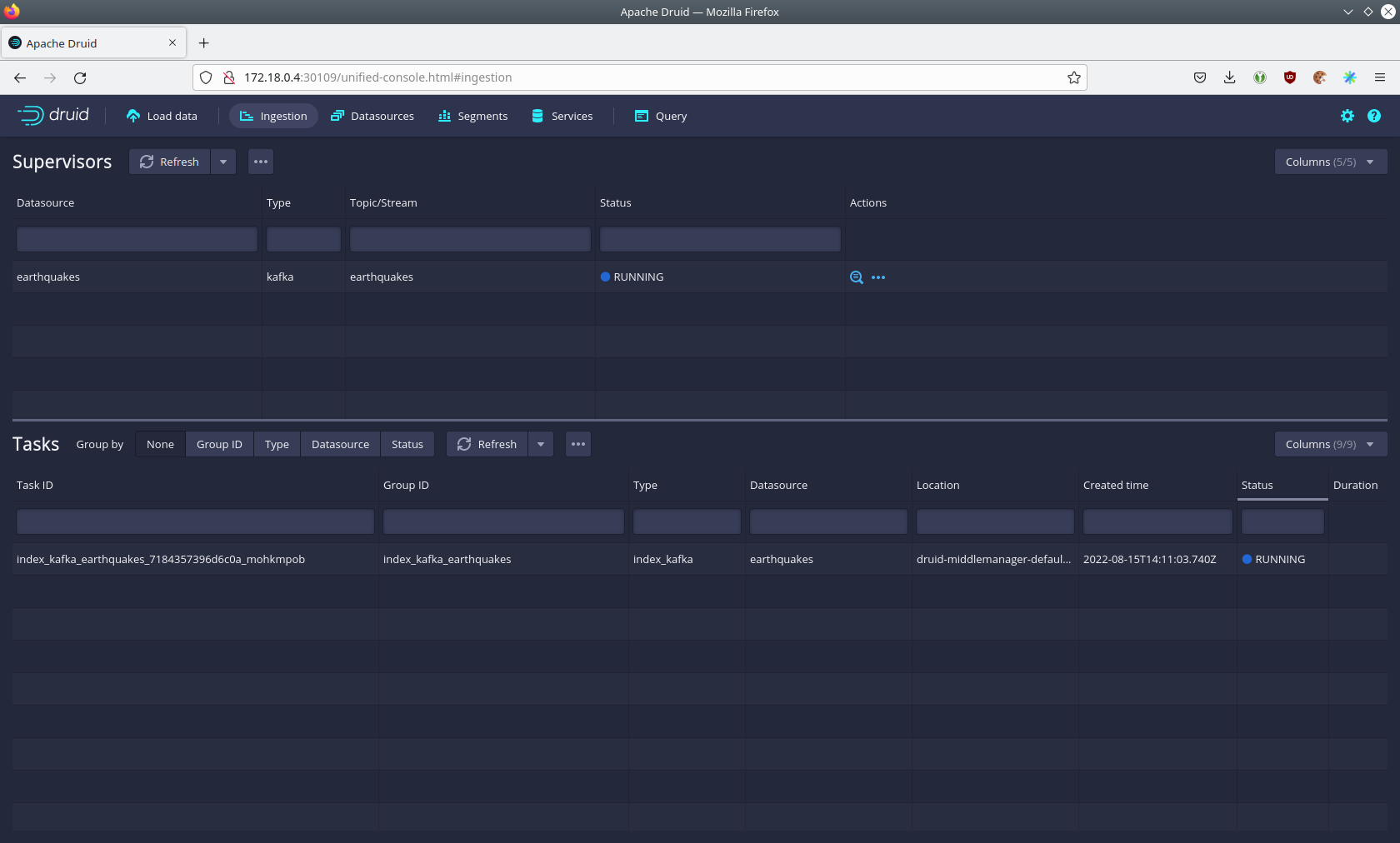
You can see additional information after clicking on the magnification glass to the right side of the RUNNING
supervisor. On the tab Statistics on the left, you can see the number of processed records as well as the number of
errors.
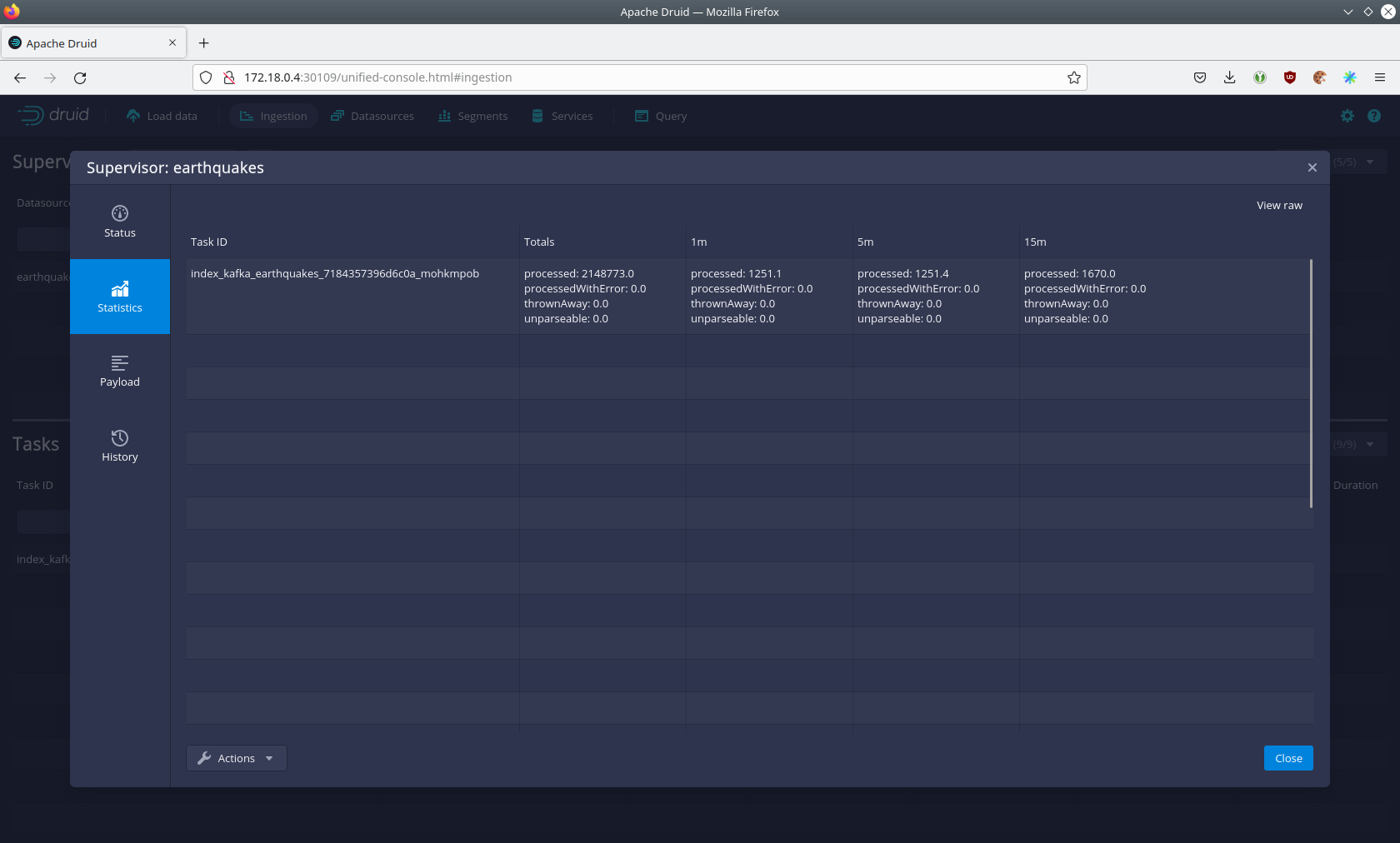
The statistics show that Druid is currently ingesting 1251 records/s and has ingested 2.1 million records already. All
entries have been consumed successfully, indicated by having no processWithError, thrownAway or unparseable
records.
Querying the Data Source
The ingestion job has automatically created the Druid data source earthquakes. You can see the available data sources
by clicking on Datasources at the top.
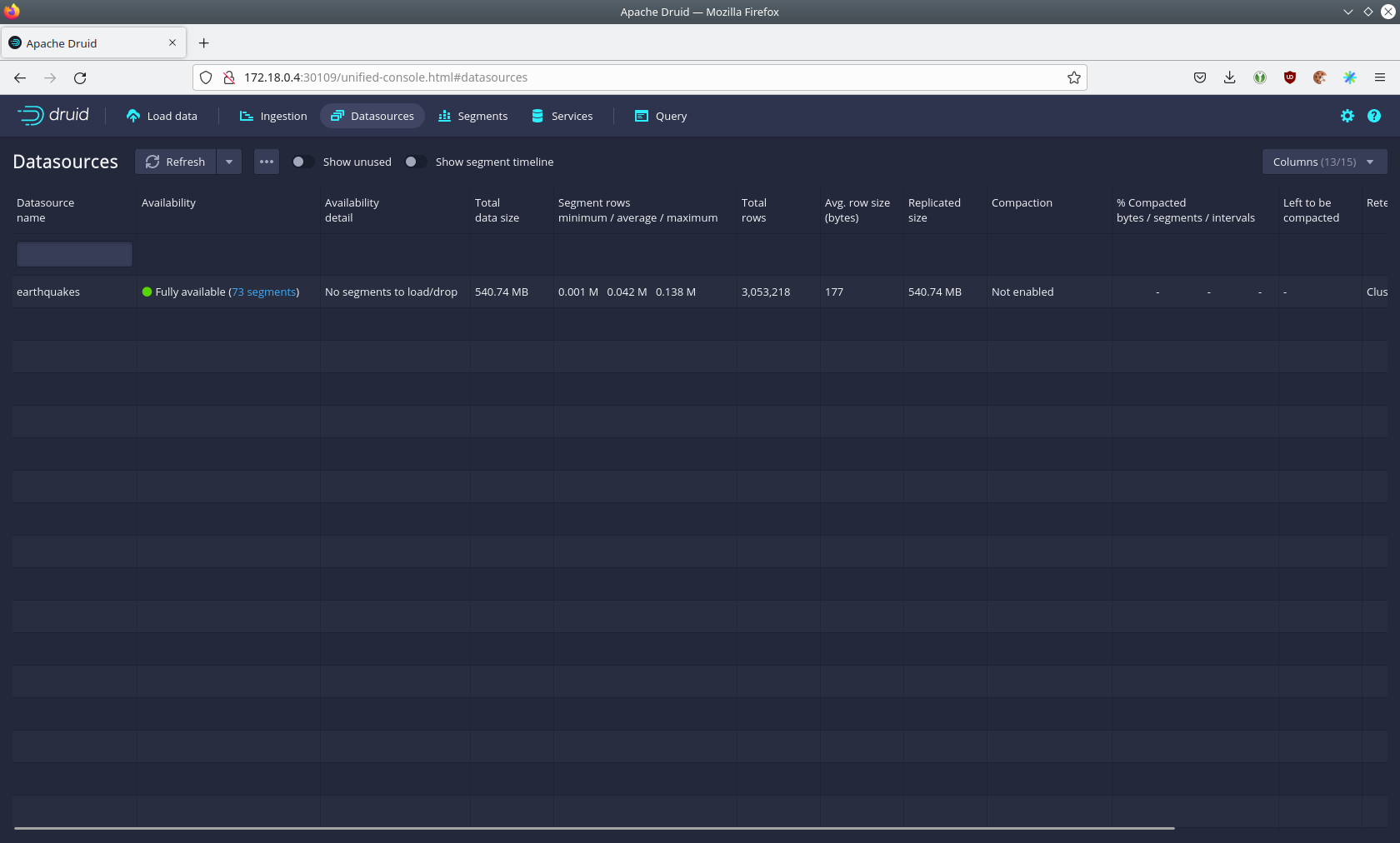
You can see the data source’s segments by clicking on the earthquake data source. In this case, the earthquake data
source is partitioned by the year of the earthquake, resulting in 73 segments.
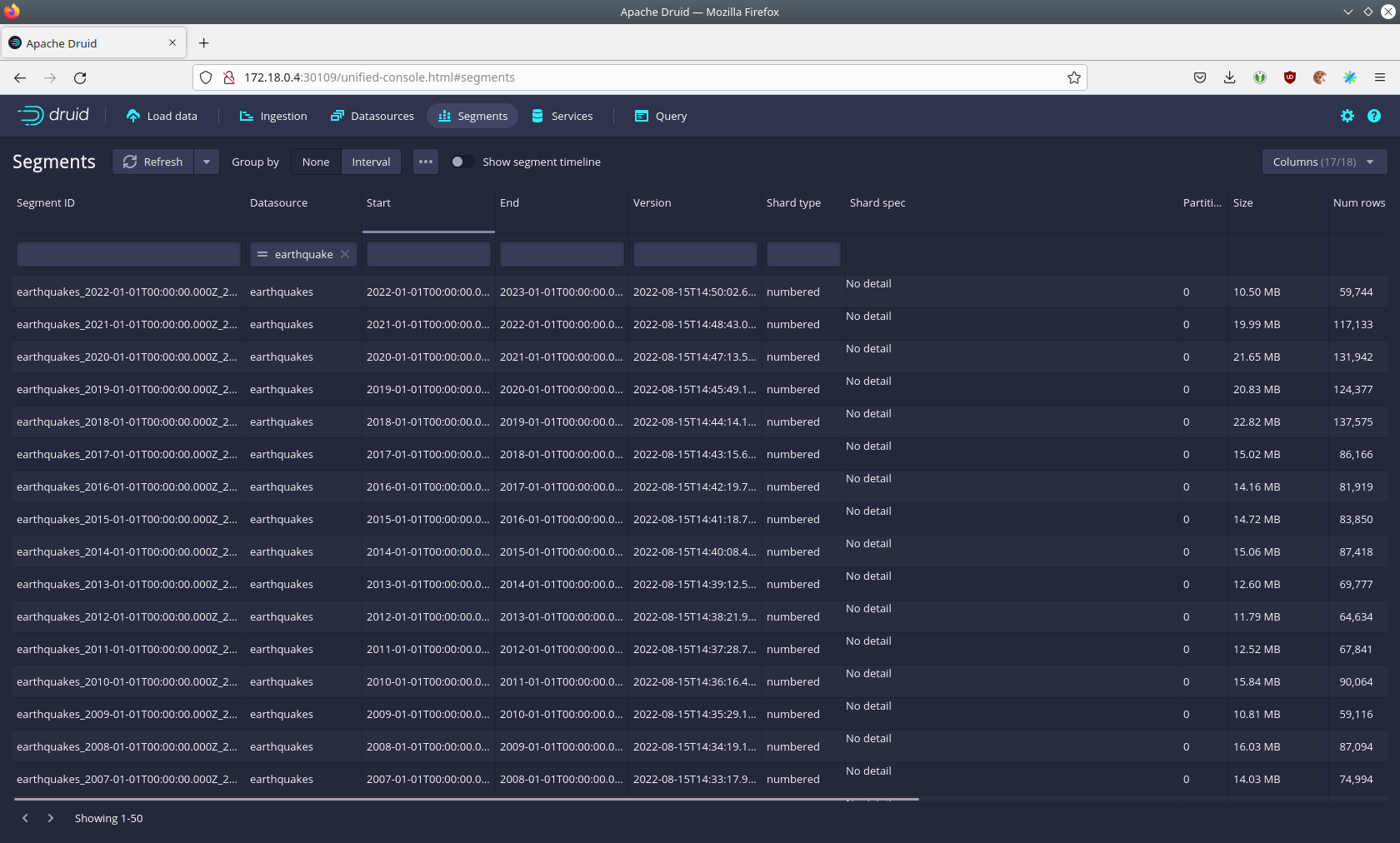
Druid offers a web-based way of querying the data sources via SQL. To achieve this, you must first click on Query at
the top.
You can now enter any arbitrary SQL statement, to e.g. list 10 earthquakes runs
select * from earthquakes limit 10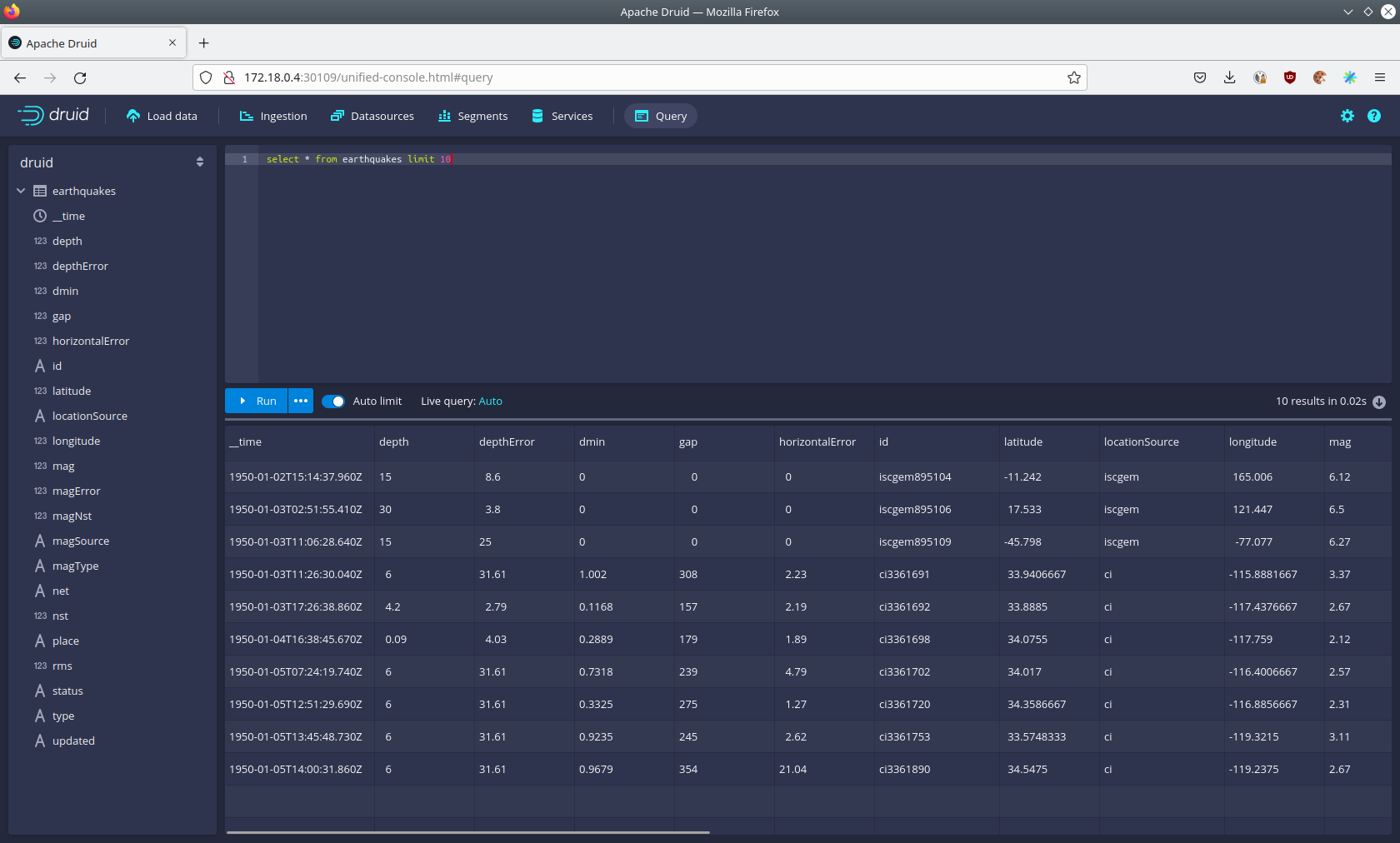
To count the number of earthquakes per year run
select
time_format(__time, 'YYYY') as "year",
count(*) as earthquakes
from earthquakes
group by 1
order by 1 desc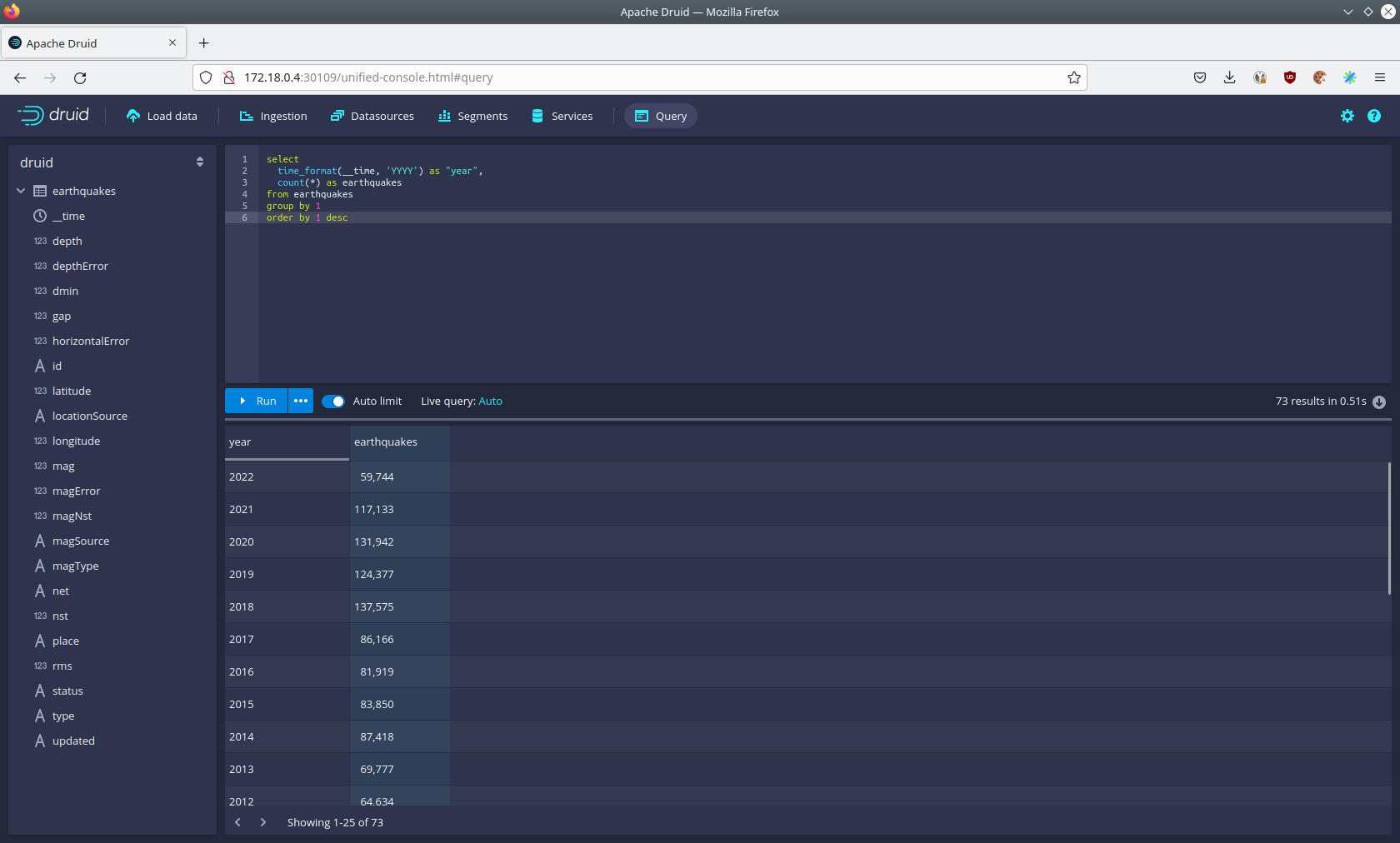
Superset
Superset provides the ability to execute SQL queries and build dashboards. Open the endpoint external-superset in your
browser (http://172.18.0.3:32108 in this case).
Log in with the username admin and password adminadmin.
Viewing Dashboard
The demo has created a Dashboard to visualize the earthquake data. To open it, click on the tab Dashboards at the top.
Click on the dashboard called Earthquakes. It might take some time until the dashboards renders all included charts.
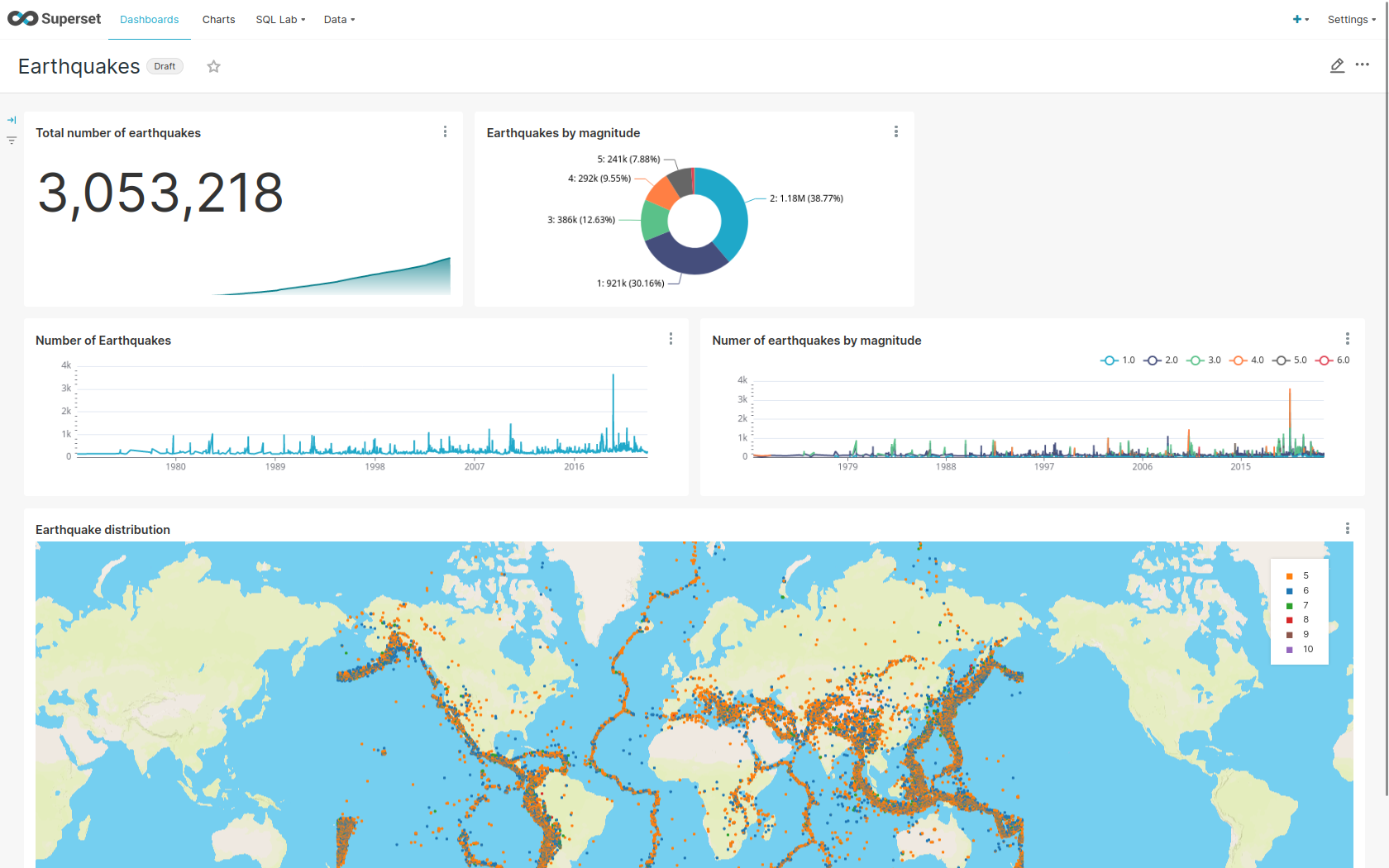
Viewing Charts
The dashboard Earthquakes consists of multiple charts. To list the charts, click on the tab Charts at the top.
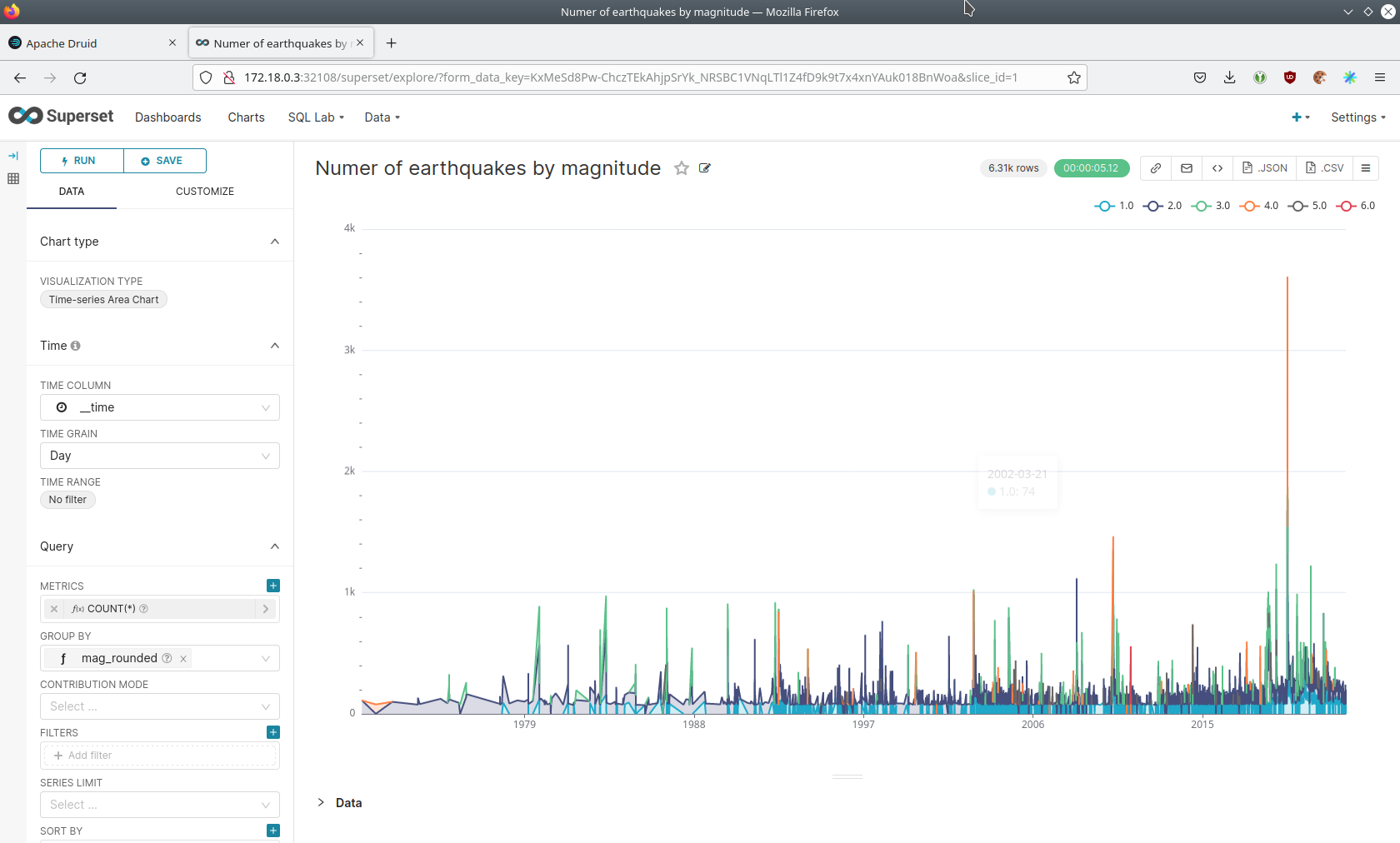
Click on the Chart Number of earthquakes my magnitude. On the left side you can modify the chart and click on Run to
see the effect.
Viewing the Earthquake Distribution on the World Map
To look at the geographical distribution of the earthquakes you have to click on the tab Charts at the top again.
Afterwards click on the chart Earthquake distribution.
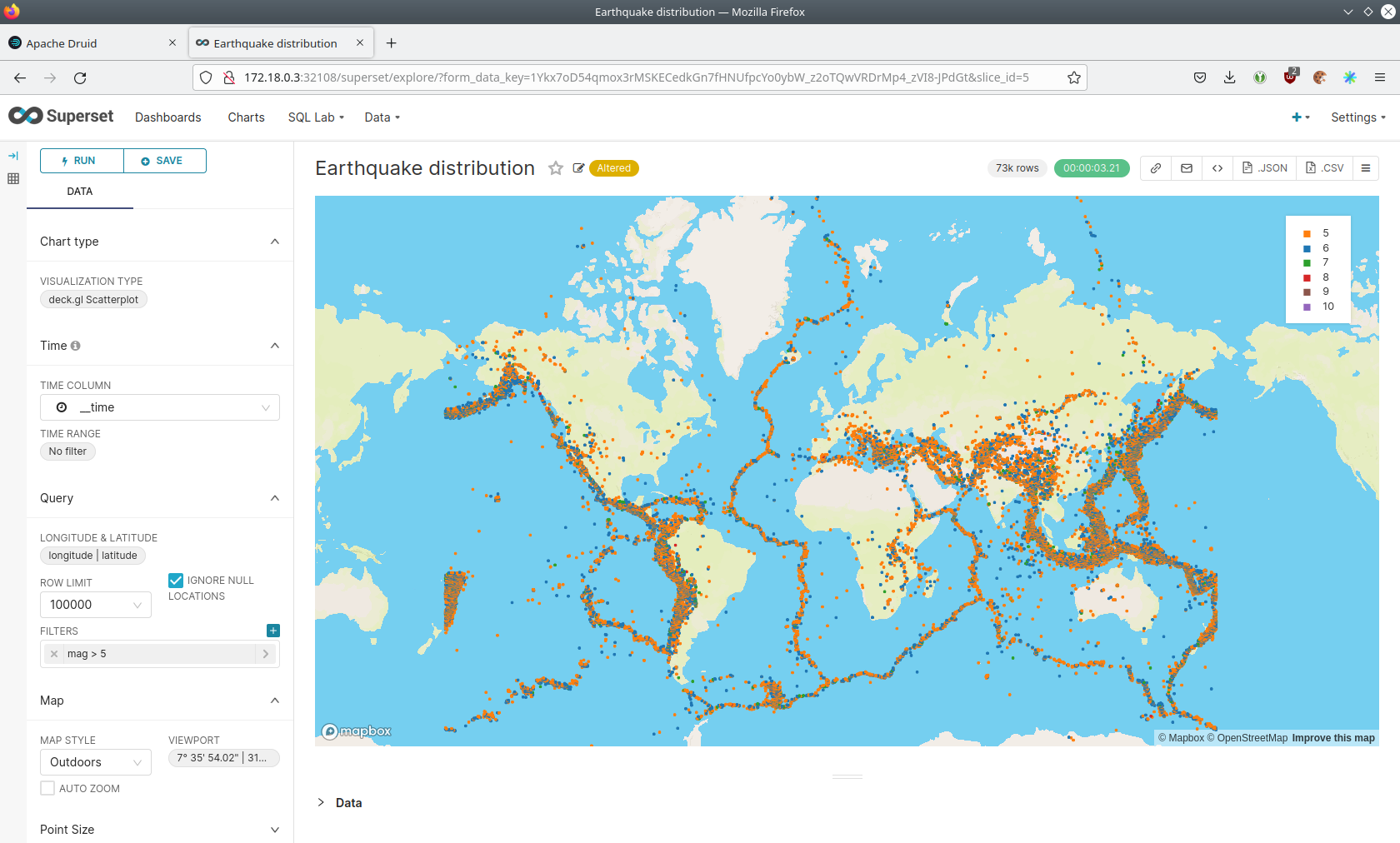
The distribution of the earthquakes matches the continental plate margins. This is the expected distribution from the Wikipedia article on Earthquakes.
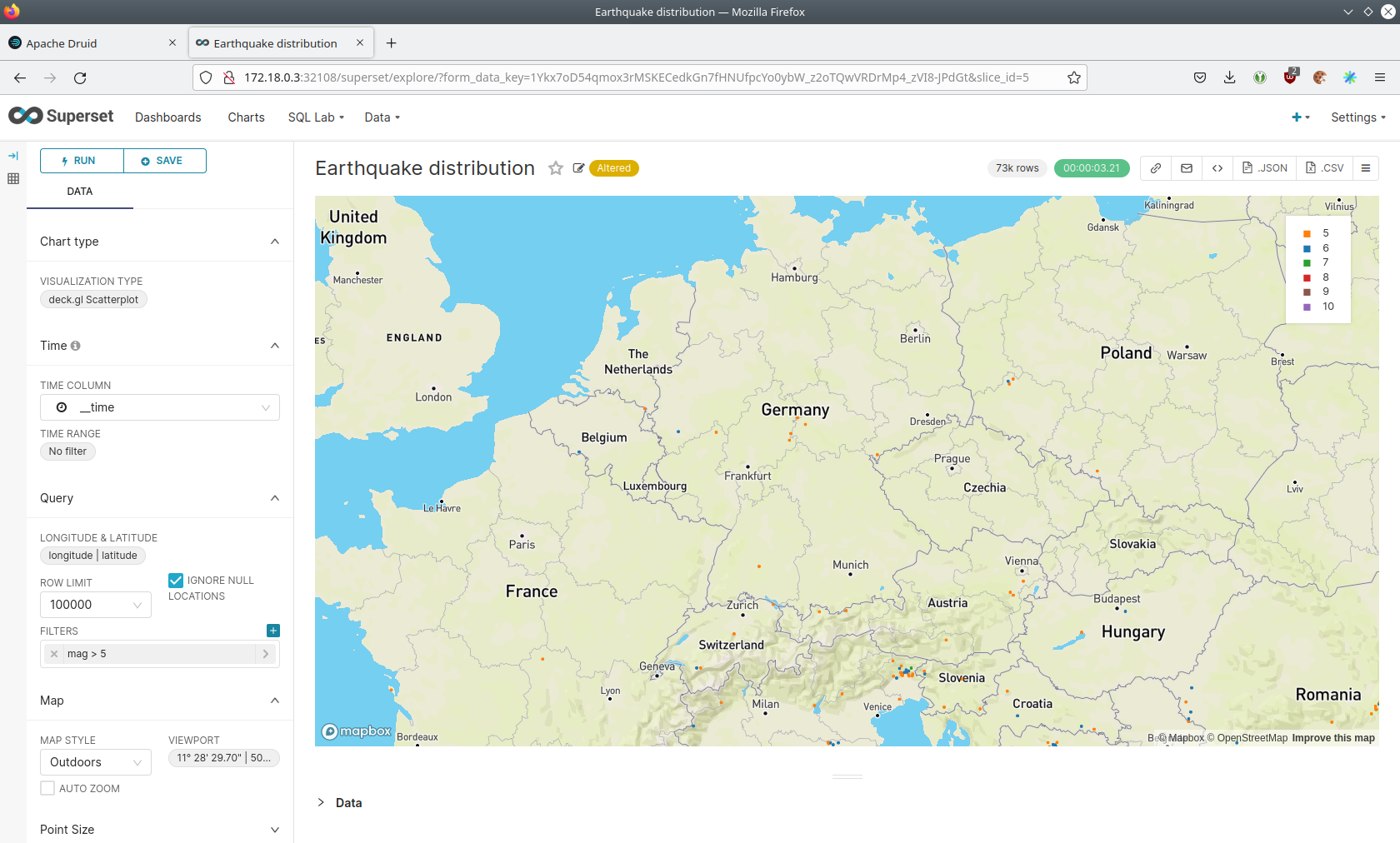
You can move and zoom the map with your mouse to interactively explore the map. You can e.g. have a detailed look at the detected earthquakes in Germany.
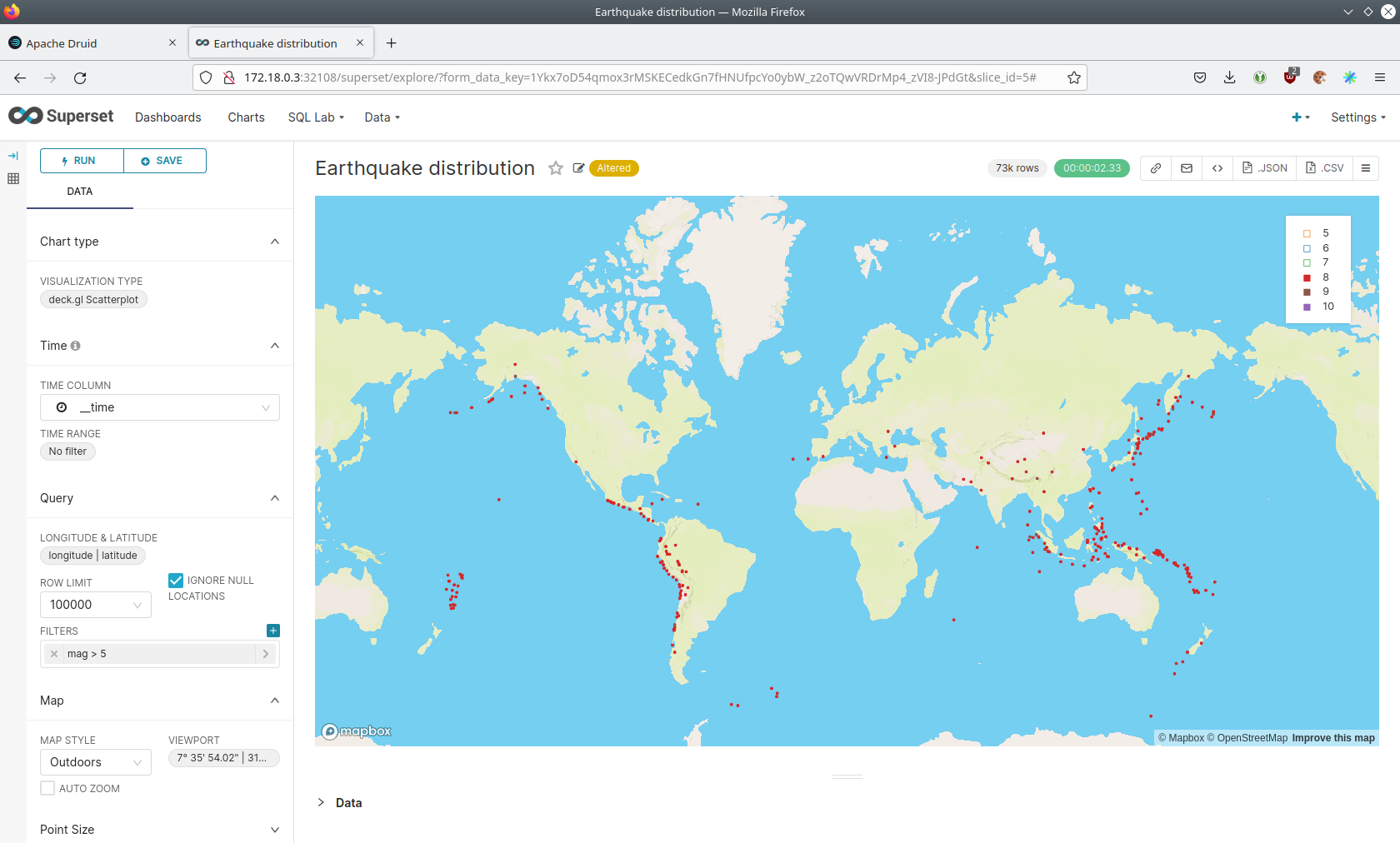
You can also click on the magnitudes in the legend on the top right side to enable/disable printing the earthquakes of that magnitude. By only enabling magnitudes greater or equal to 8 you can plot only the most severe earthquakes.
Executing Arbitrary SQL Statements
Within Superset you can not only create dashboards but also run arbitrary SQL statements. On the top click on the tab
SQL Lab → SQL Editor.
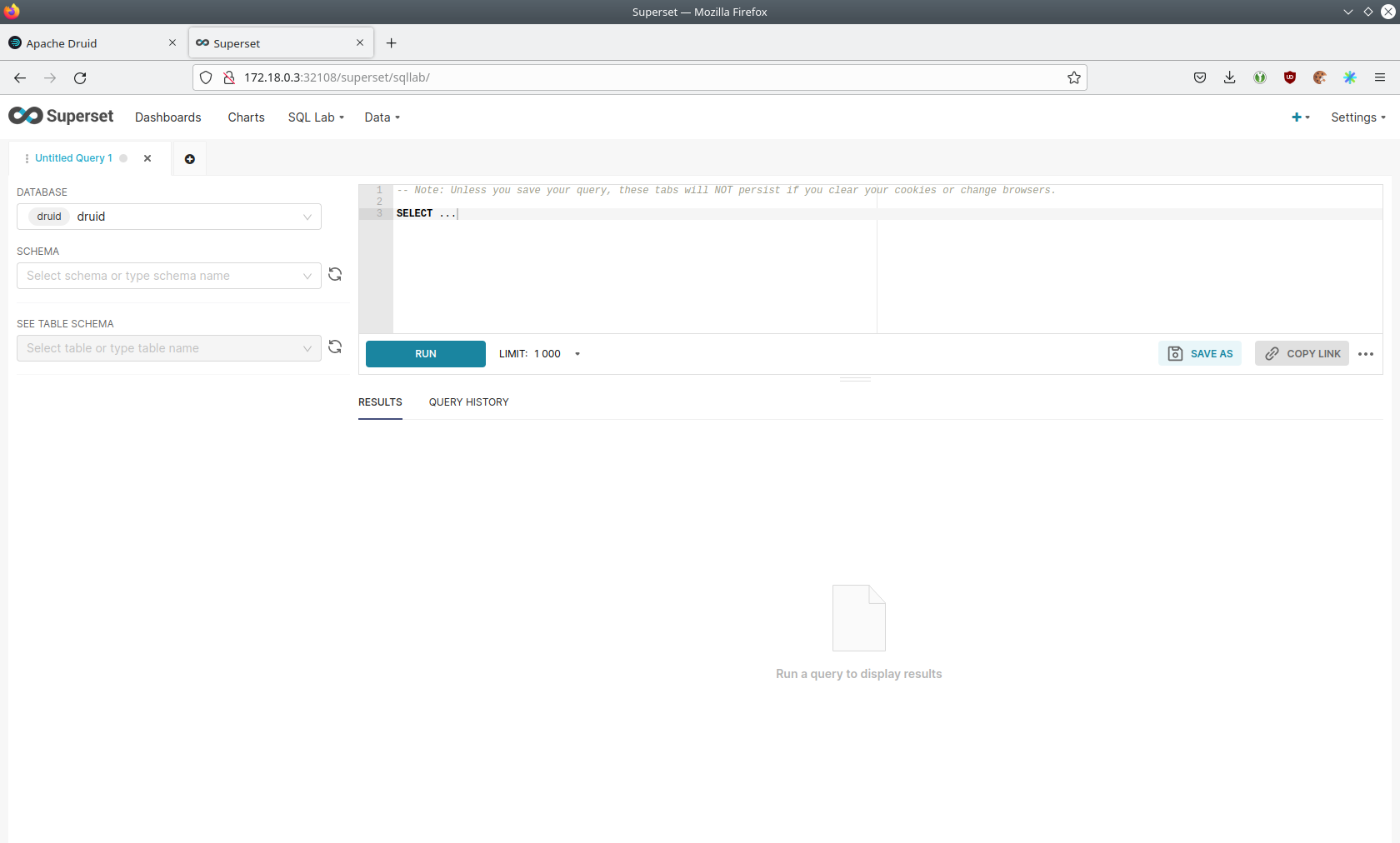
On the left select the database druid, the schema druid and set See table schema to earthquakes.
On the right textbox enter the desired SQL statement. If you do not want to make one up, you can use the following:
select
time_format(__time, 'YYYY') as "year",
count(*) as earthquakes
from earthquakes
group by 1
order by 1 desc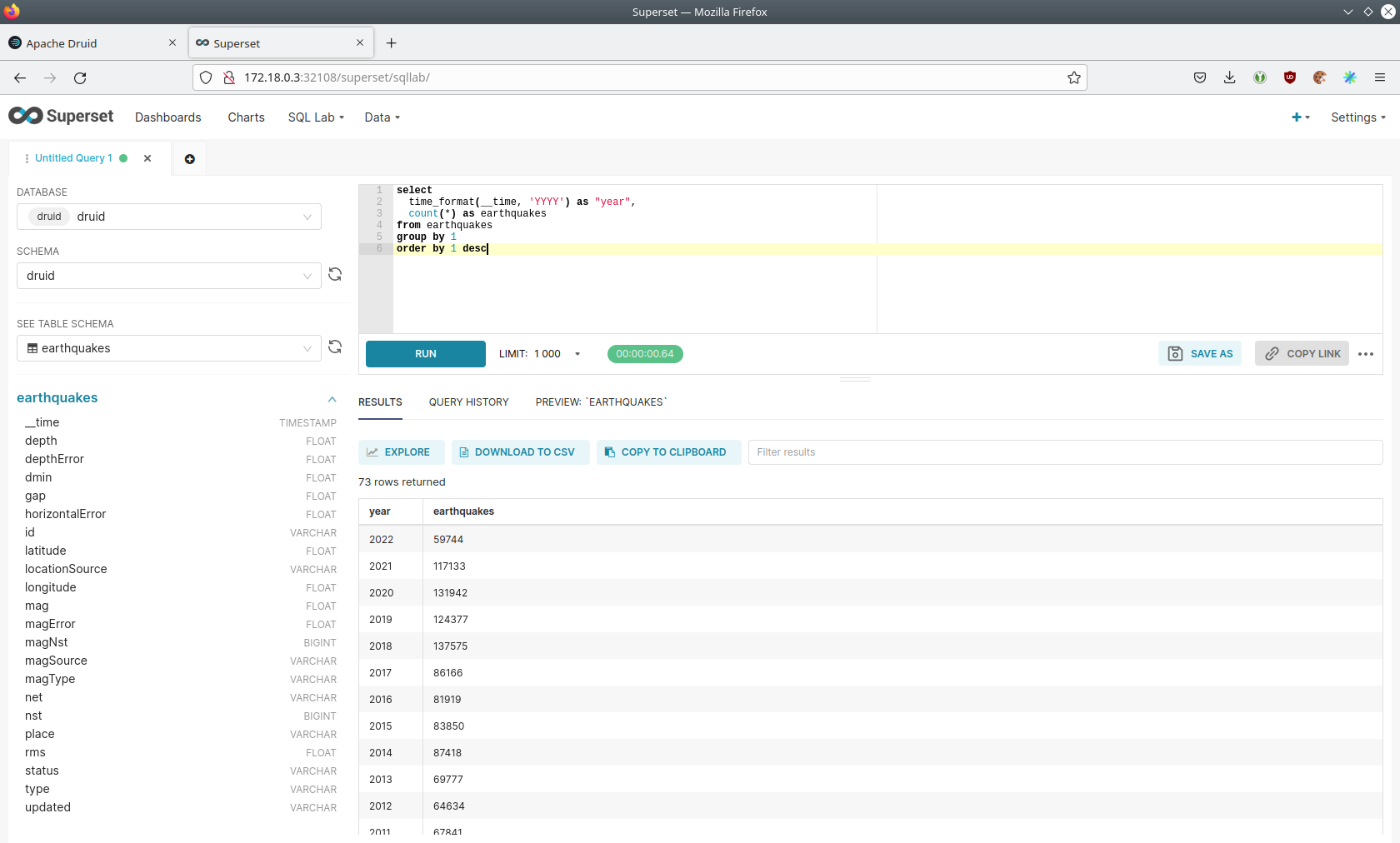
MinIO
The S3 provided by MinIO is used as a persistent deep storage for Druid to store all the data used. Open the minio
endpoint console-http in your browser (http://172.18.0.4:31664 in this case).
Log in with the username admin and password adminadmin.
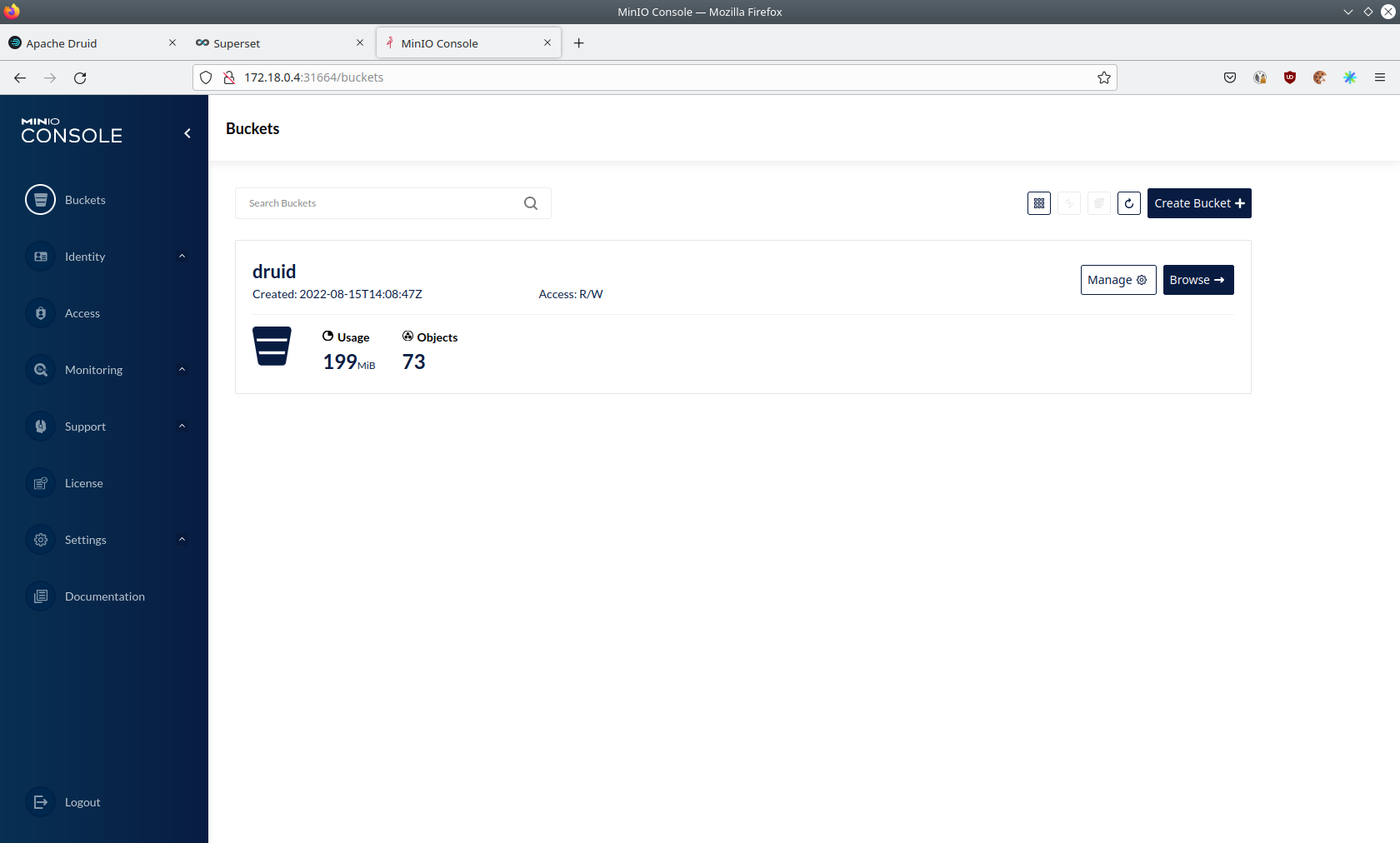
Click on the blue button Browse on the bucket druid and open the folders data → earthquakes.
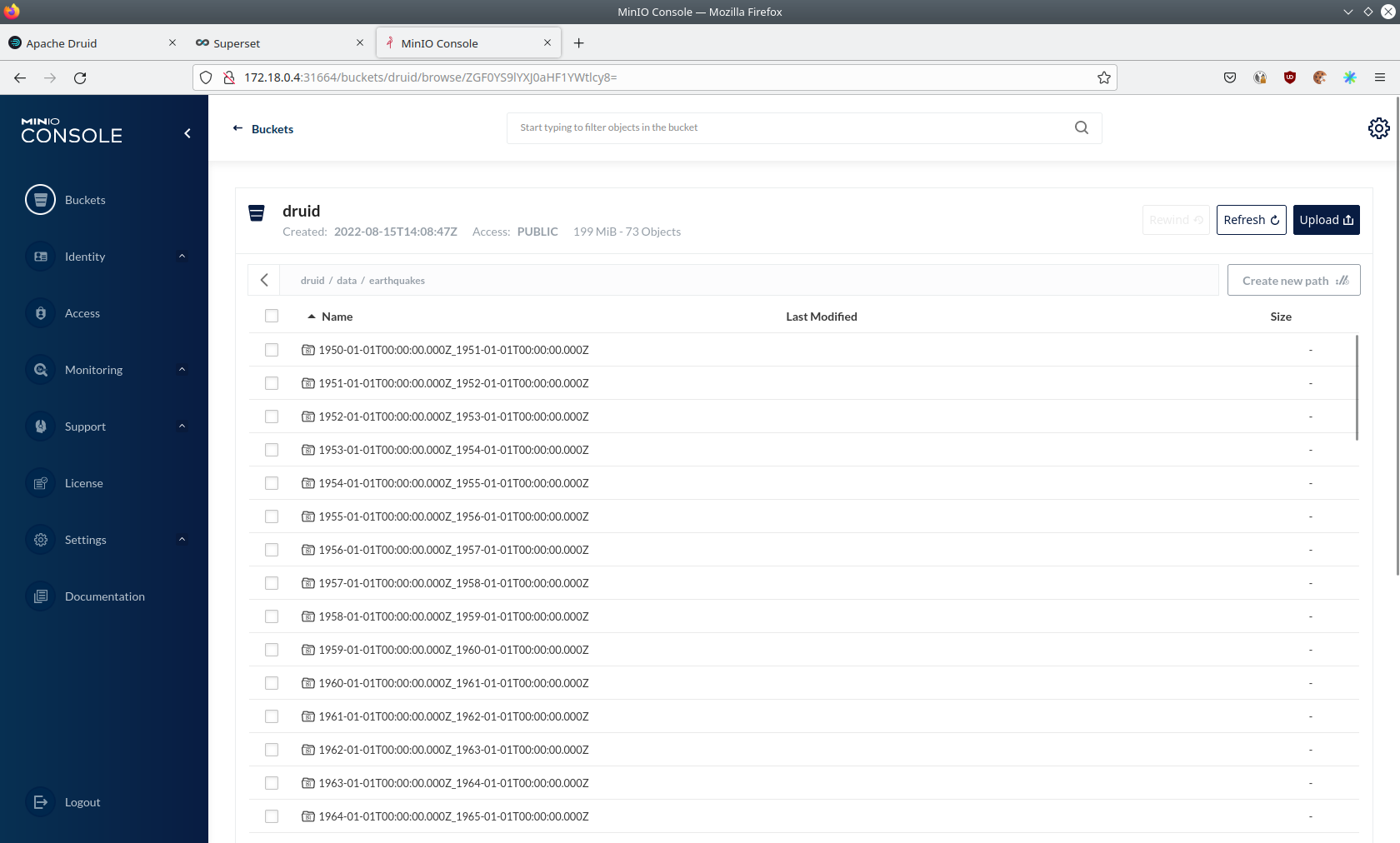
As you can see druid saved 199MB of data within 73 prefixes (folders). One prefix corresponds to on segment which in turn contains all the data of a year. If you don’t see any folders or files, the reason is that Druid has not saved its data from memory to the deep storage yet. After waiting a few minutes, the data should have been flushed to S3 and show up.
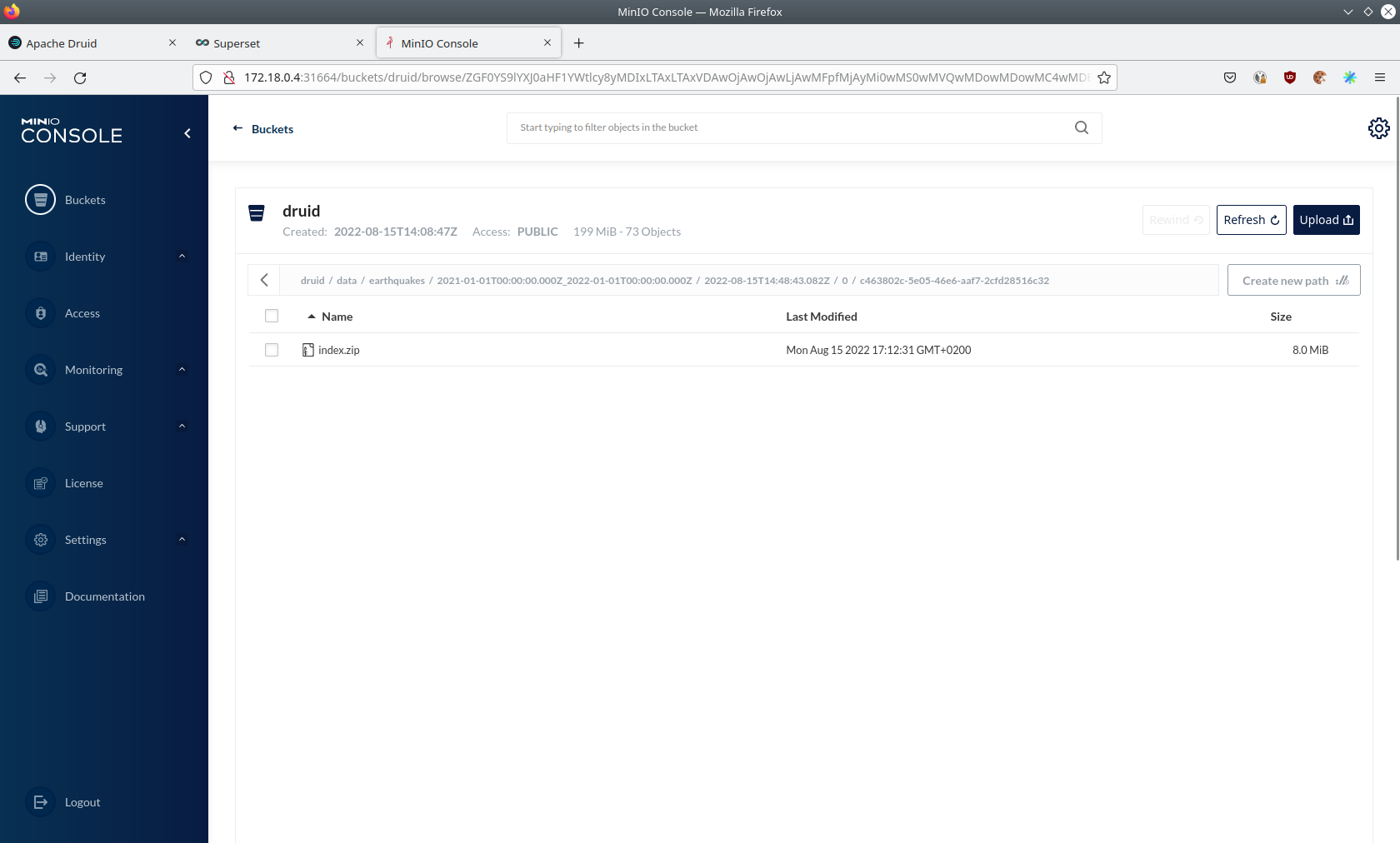
If you open up a prefix for a specific year you can see that Druid has placed a file containing the data of that year there.
Summary
The demo streamed 10,000 earthquake records/s for a total of ~3 million earthquakes into a Kafka steaming pipeline. Druid ingested the data near real-time into its data source and enabled SQL access to it. Superset was used as a web-based frontend to execute SQL statements and build dashboards.
Where to go from here
There are multiple paths to go from here. The following sections give you some ideas on what to explore next. You can find the description of the earthquake data on the United States Geological Survey website.
Executing Arbitrary SQL Statements
Within Superset (or the Druid web interface), you can execute arbitrary SQL statements to explore the earthquake data.
Creating Additional Dashboards
You also can create additional charts and bundle them together in a Dashboard. Have a look at the Superset documentation on how to do that.
Loading Additional Data
You can use the NiFi web interface to collect arbitrary data and write it to Kafka (it’s recommended to use new Kafka topics for that). Alternatively, you can use a Kafka client like kafkacat to create new topics and ingest data. Using the Druid web interface, you can start an ingestion job that consumes and stores the data in an internal data source. There is an excellent tutorial from Druid on how to do this. Afterwards, the data source can be analyzed within Druid and Superset, like the earthquake data.